Facts About the Allergic Rhinitis
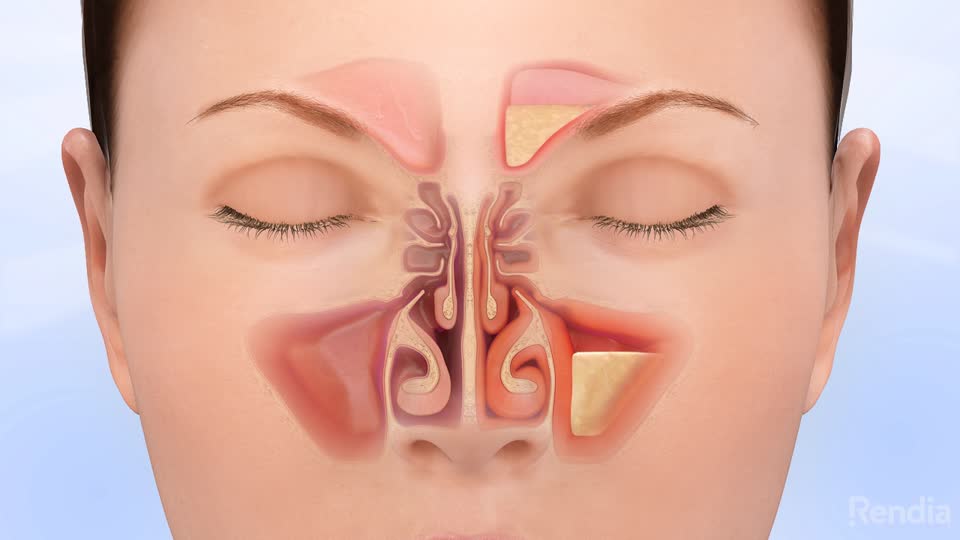
Table of Contents
What is allergic rhinitis?
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that causes an allergic reaction. Allergic rhinitis, or hay fever, is an allergic response to specific allergens. Pollen is the most common allergen in seasonal allergic rhinitis. These are allergy symptoms that occur with the change of seasons.
Nearly 8 percent of adults in the United States experience allergic rhinitis of some kind, according to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI). Between 10 and 30 percent of the worldwide population may also have allergic rhinitis.
Causes
Allergic rhinitis is an allergic condition like asthma, meaning that the body tends to overreact to certain types of outside substances. One way it overreacts is by producing antibodies that signal your immune system to release histamine and other chemicals. These chemicals cause the symptoms of allergic rhinitis including sneezing, itchy or runny nose, itchy or watery eyes, and even coughing.
Allergic rhinitis can be inherited, but you probably don’t inherit particular allergies, such as to cat dander or ragweed. Instead, you just inherit the tendency to be allergic. Children have a 30% to 60% chance of developing allergic rhinitis if one of their parents is affected and a 50% to 70% chance if both parents have allergic rhinitis.
Symptoms and Complications
Most people with allergic rhinitis know they have it, although it can sometimes be confused with the common cold.
Symptoms include runny nose; sneezing; itchy nose, mouth, throat, or eyes; and congestion. Other symptoms can also occur, such as tearing of the eyes, coughing, sore throat, wheezing, and headache.
People with mild allergic rhinitis have symptoms but they are not troublesome and do not interfere with daily activities such as school, work, or sleep. With moderate/severe allergic rhinitis, the symptoms are troublesome and affect daily life.
Treatment and Prevention
The best way to prevent allergic rhinitis is to avoid the allergen. This may mean changing your habits, or even giving away a pet or moving to another house if the symptoms are unbearable and don’t respond to medications.
Here are some tips you can try to minimize exposure to allergens:
Pollen:
- Keep windows and doors closed
- When using air conditioning, use the indoor cycle
- Shower/bathe after outdoor activity to remove pollen from your hair and skin
- Monitor the pollen count. Try to avoid going outside when the pollen count is high.
Indoor molds:
- Avoid using humidifiers and cool mist vaporizers, as mold often grows in them. If you must use them, clean them often.
- Do not put carpet or furniture in your basement if it is damp or prone to flooding
- Remove houseplants (a common source of mold)
Dust mites:
- Avoid carpeting your bedroom and main living areas
- Clean while the allergic person is not at home, or if the allergic personal must do the cleaning, have them wear a facemask
- Wash bedding in hot water (>55 °C) at least every other week.
- Use zippered, allergen-proof casings on mattresses, box springs and pillows
Keep in mind that it is not always possible to control the environment or to eliminate or avoid allergens, especially those that are airborne. Many people need medication treatment for relief. Fortunately, most people respond well to medications.
The therapy of choice will depend on your symptoms, the severity of your symptoms, your past response to medications, and other medical conditions that you have, if any.
Treatment for mild symptoms is usually antihistamines taken orally (e.g., chlorpheniramine*, diphenhydramine, cetirizine, loratadine, fexofenadine, desloratadine, bilastine). Your doctor or pharmacist can help you choose the medication best suited to your needs.
For example, many oral antihistamines are now “non-drowsy.” People with certain medical conditions (e.g., glaucoma, prostate problems) should consult their doctor before using certain antihistamines. Antihistamine nose sprays (e.g., levocabastine) and eye drops (e.g., olopatadine) are also available and may be useful for nasal and eye symptoms respectively.
Sometimes decongestants (oral and nasal) may be used for nasal congestion. However, nasal decongestant use should be limited to 3 days, otherwise it may make the symptoms worse. Seeking advice from a health professional is recommended as those with medical conditions such as high blood pressure must use caution with decongestants.
A corticosteroid nose spray (e.g., budesonide, ciclesonide, fluticasone, flunisolide, mometasone) can be tried if antihistamines aren’t working. Corticosteroid sprays can be used if rhinitis symptoms are chronic and are the preferred treatment for symptoms that are moderate to severe.
An anticholinergic nose spray (e.g., ipratropium) may also be used to help reduce runny nose symptoms. Saline nose sprays and lubricant eye drops may also help with nose and eye symptoms.
Women who are pregnant or breast-feeding and children should consult their doctor or pharmacist before beginning treatment for allergic rhinitis.
If allergen avoidance and medical treatment for allergic rhinitis aren’t effective, allergen immunotherapy may be an option. Allergen immunotherapy can be given as shots or as pills placed under the tongue. With shots, small amounts of the allergen are injected regularly while slowly increasing the dosage.
The hope is that the immune reaction becomes weaker and weaker as the body gets used to the presence of the allergen. Rarely, the person may have a system wide immune reaction called anaphylaxis, which can be fatal. People receiving allergen immunotherapy have to wait in the clinic with a physician present for half an hour after each shot in case there is a reaction.
Immunotherapy pills placed under the tongue are taken daily. These pills are less likely to cause anaphylaxis but are only available for certain types of allergies. The first dose is taken at the doctor’s office, after which subsequent doses can be taken at home.
For any important information please contact us Email GadgetsNg info@gadgetsng.com
[Button id="1"]



п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india https://indiaph24.store/# reputable indian pharmacies
india pharmacy